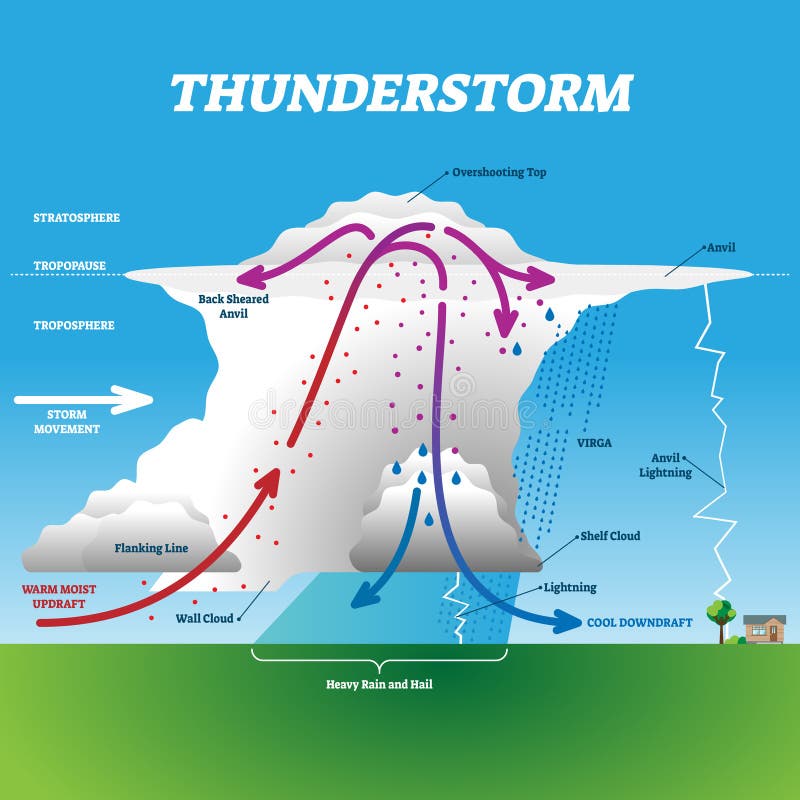
What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like . Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity are significantly higher. the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km). The main difference between the two is the. — meteorologists convey the chance of cloud cover or rain in percentages, but what those numbers mean in the real world isn’t always. — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area. — meteorologist ari sarsalari breaks down the difference.
from www.dreamstime.com
Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area. Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity are significantly higher. 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km). The main difference between the two is the. the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. — meteorologists convey the chance of cloud cover or rain in percentages, but what those numbers mean in the real world isn’t always. The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. — meteorologist ari sarsalari breaks down the difference.
Thunderstorm Vector Illustration. Labeled Educational Wind Cloud
What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km). The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity are significantly higher. — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. — meteorologists convey the chance of cloud cover or rain in percentages, but what those numbers mean in the real world isn’t always. the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km). The main difference between the two is the. — meteorologist ari sarsalari breaks down the difference. — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area.
From sciencestruck.com
A Quick Glance at the Causes and Effects of Thunderstorms Science Struck What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity are significantly higher. — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area.. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From a-z-animals.com
Scattered Thunderstorms Meaning Explaining Their Nature and Impact A What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area. — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. 14.1 & 14.2). What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From secretlosangeles.com
L.A. Had A Striking Thunderstorm And Here Are The Breathtaking Pictures What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like The main difference between the two is the. — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km). Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area. — the key difference between. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From www.thoughtco.com
What Is a Thunderstorm? What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km). — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. — meteorologists convey the chance of cloud cover or rain in percentages, but what those numbers mean in the real world isn’t always. . What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From nwafoundation.org
Severe Thunderstorms & Severe Thunderstorm Safety National Weather What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km). the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. The main difference between the two is the. — meteorologist ari sarsalari breaks down the difference. — what does. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From a-z-animals.com
Scattered Thunderstorms Meaning Explaining Their Nature and Impact A What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — meteorologist ari sarsalari breaks down the difference. — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area. 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From www.dailymail.co.uk
Incredible timelapse footage of supercell storm forming over Kansas What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km). Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From lakelandconnect.net
Severe thunderstorm watch for the Lakeland Lakeland Connect What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km).. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From mentalfloss.com
What's The Difference Between Scattered And Isolated Thunderstorms What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity are significantly higher. Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area. — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. the simplest thunderstorm (see. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From www.worldatlas.com
Top Facts About Thunderstorms WorldAtlas What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity are significantly higher. the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. — meteorologists convey the chance of cloud cover or rain in percentages, but what those numbers mean in the real world isn’t. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From mike-knavarro.blogspot.com
Which Best Describes the Causes of a Thunderstorm What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to its depth (of order 10 to 15 km). The main difference between the two is the. Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From www.washingtonpost.com
Isolated vs. scattered vs. widespread thunderstorms What’s the What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? The main difference between the two is the. — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. — meteorologists convey the chance of cloud cover or rain in percentages, but what those numbers mean in the real world isn’t always. — the key difference between isolated and scattered. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From theweatherstationexperts.com
The Difference Between Isolated and Scattered Thunderstorms What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area. — meteorologist ari sarsalari breaks down the difference. the simplest thunderstorm (see figs. The main difference between the two is the. — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. 14.1 & 14.2) has a nearly vertical stem of diameter roughly equal to. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From www.britannica.com
Thunderstorm Definition, Types, Structure, & Facts Britannica What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups. — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From www.e-education.psu.edu
Multicell and Supercell Thunderstorms METEO 3 Introductory Meteorology What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity are significantly higher. — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). The main difference between the two is the. Scattered thunderstorms are more numerous in nature and cover a larger area. — meteorologists. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From www.dailypress.com
Scattered thunderstorms in Saturday's forecast Daily Press What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — the key difference between isolated and scattered thunderstorms is the coverage area. The main difference between the two is the. Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity are significantly higher. — meteorologist ari sarsalari breaks down the difference. — what does scattered thunderstorms mean? — isolated thunderstorms occur alone, while scattered thunderstorms occur in groups.. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From www.nssl.noaa.gov
Severe Weather 101 Thunderstorm Basics What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like The main difference between the two is the. — meteorologists convey the chance of cloud cover or rain in percentages, but what those numbers mean in the real world isn’t always. The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus (latin for anvil). — the key difference between isolated and. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.
From allthedifferences.com
Isolated vs. Scattered Thunderstorms Explaining the Variations in What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like — meteorologist ari sarsalari breaks down the difference. Here, your chances of seeing thunderstorm activity are significantly higher. — meteorologists convey the chance of cloud cover or rain in percentages, but what those numbers mean in the real world isn’t always. The large top is called the anvil, anvil cloud, or thunderhead, and has the official name incus. What Does Scattered Thunderstorms Look Like.